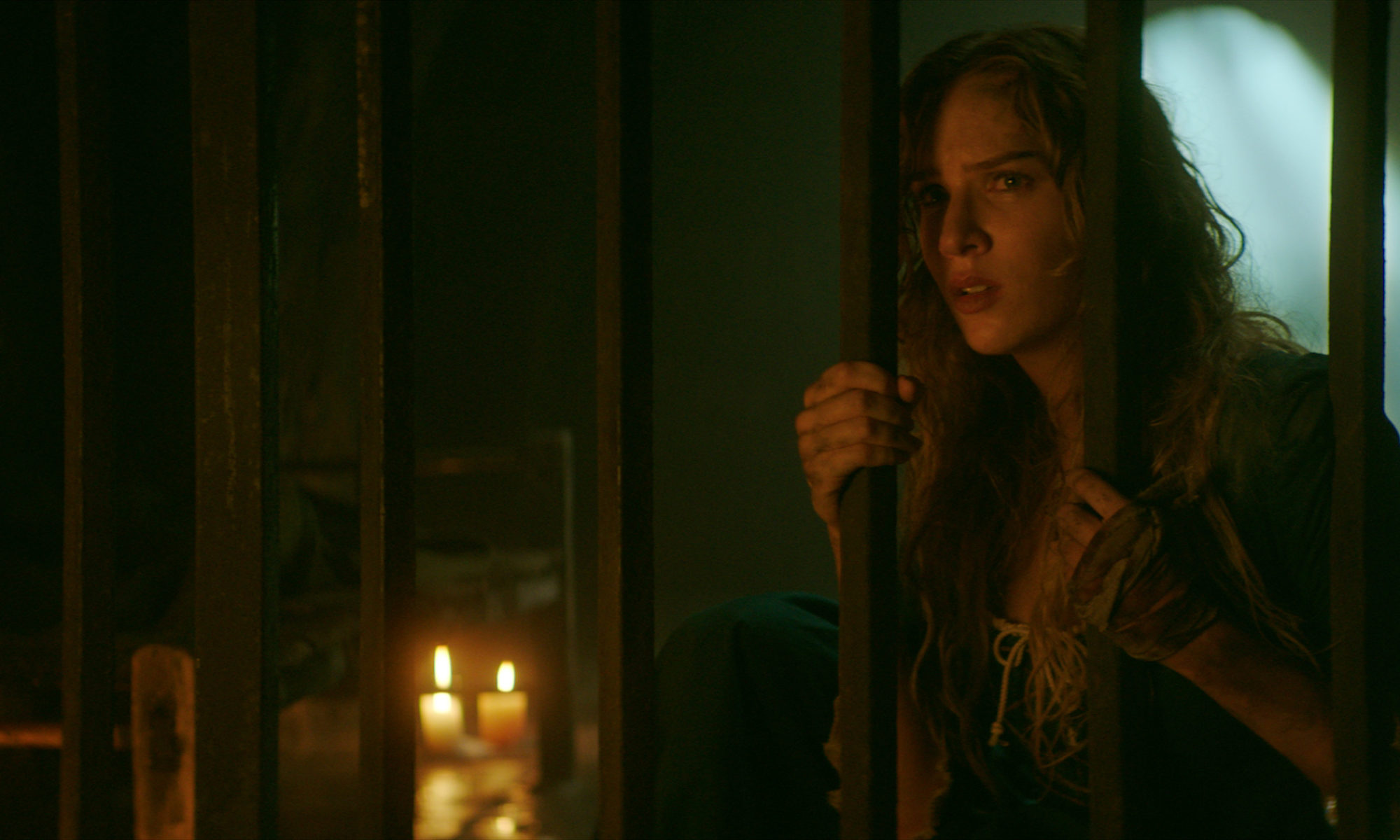Continue reading
Tintorera
25/100For what must be the majority of its running time, Tintorera is a sun-and-skin melodrama set in a Mexican resort village where the loitering Steven and Miguel (Hugo Stiglitz and Andrès Garcia) navigate the treacherous waters of a sexy threesome with an English tourist, Gabriella (Susan George), who declares that the only thing off-limits in their relationship … is love. By contrast, about a third of the film is a skeevy underwater adventure-cum-travelogue in which Steven, Miguel, and other local fisherman absolutely have their way with the aquatic kingdom, skewering barracudas and manta rays and using them as bait for larger fish, hanging sea tortoises off the side of boats and slashing them open for blood chum, and cutting open tiger sharks and letting them bleed out on the ocean floor. (Seriously, this movie never met a fish it didn’t want to stab in the face.) And then, for just a few fleeting moments at a time, Tintorera is one of the great killer-shark movies, with underdressed women and overconfident men getting torn apart in mid-swim before the shark flees the scene with a head or torso clutched in its jaws like a happy spaniel carrying a pheasant, entrails dragging behind and gallons of blood saturating the waters behind them.
Continue readingThe Reckoning
44/100Imagine a downbeat cross between historical romance, rape-revenge thriller and what’s become known as folk horror and you’ll have a pretty good idea of the overall mood of The Reckoning. Writer-director Neil Marshall, who made a splash as a genre director back in the early 2000s with Dog Soldiers (werewolves vs army men) and Sundance smash The Descent (CHUDs vs spelunkers), casts co-writer Charlotte Kirk as Grace Haverstock, a woman unjustly accused of witchcraft after the death of her husband during the English plague epidemic of 1665. After Grace rebuffs the advances of local squire, landlord and sex pest Pendleton (Steven Waddington), he helps convince the townspeople that she must be a witch, summoning Judge Moorcroft (Sean Pertwee, trying his best to crawl out from under Vincent Price’s indelible Witchfinder General performance) to elicit her confession of heresy.
Continue readingKnocking
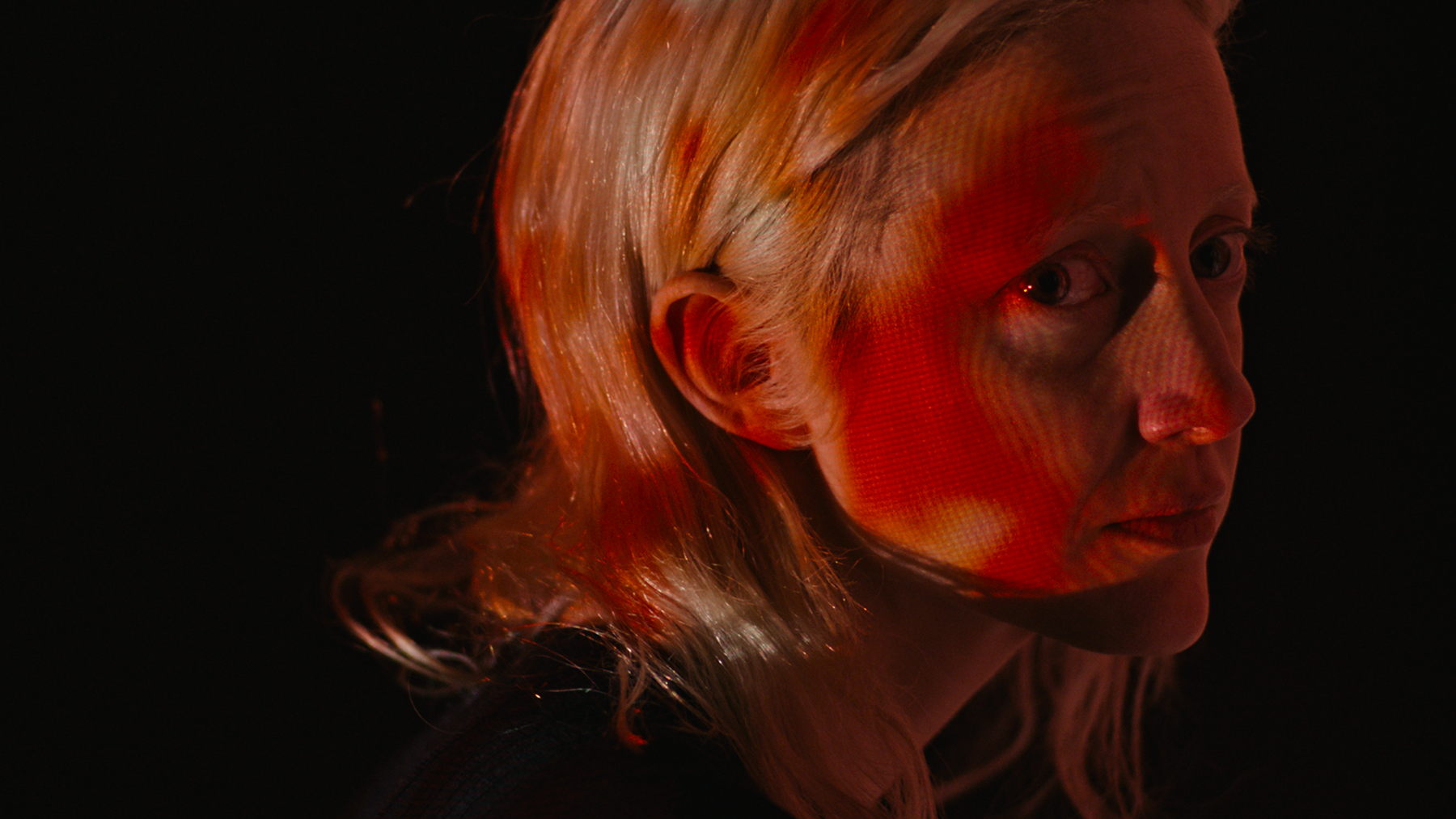
75/100A woman living alone in a drab apartment block may or may not be losing her mind in Knocking, the feature film debut of Swedish documentarian Frida Kempff. The details of the story are nothing new (it draws on sources as disparate as Persona, Repulsion, Mulholland Dr. and Requiem for a Dream) but Kempff’s own vision is unmistakeable. Distinguished by striking frame compositions and camera moves as well as a perfectly balanced lead performance by Cecilia Milocco, Knocking is a modest powerhouse — a threadbare narrative that’s gorgeously shot, beautifully performed and spooky as hell.
Continue readingCensor
54/100For a roughly 20-year period beginning in the early 1980s, low-budget horror films were considered a primary threat to the safety of the British public. While reliably puritanical Americans were scandalized by the lyrics to “Darling Nikki,” their British counterparts were shocked and appalled by a slate of so-called “video nasties” — generally low-budget exploitation films that ranged from the ripe theatrics of Herschell Gordon Lewis’s Blood Feast to the grim sexual violence of The Last House on the Left and the Nazisploitation cycle that included such prosaic titles as Love Camp 7, Gestapo’s Last Orgy and The Beast in Heat. Following years of pressure from tabloids and special-interest groups who insisted these titles were corrupting the populace, the conservative government began applying stricter censorship standards to video releases, spurring the British Board of Film Classification (BBFC) to demand that certain scenes be trimmed or eliminated from even adults-only titles (rated “18”) or denying certification altogether. Selling or renting unclassified videos became a criminal offense.
Continue readingPossessor
95/100Possessor opens with a glossy murder sequence that seems to be the jumping-off point for a glossy techno-thriller. The killer is revealed to be an assassin who operates by taking over the minds of working-class stiffs who are in a position to be close enough to various VIPs to carry out quick hits. Each unlucky prole chews on a bullet as the possessor controlling their actions blinks out of the equation and returns to her own body. Having established the kind of killer premise that an enterprising show-runner could use as fodder for two, maybe three seasons of a Netflix original, the film gets restless and almost immediately veers into uncharted territory, as the apparently imperturbable killer Tasya Vos (tough, wiry and tender Andrea Riseborough) reveals herself to be distracted by concerns over her disintegrated family life-and perhaps unfit to fight back when one of her meat puppets, a rank-and-file big-tech employee named Colin (Christopher Abbott), manages to rebel against her control.
Continue readingTotal Recall
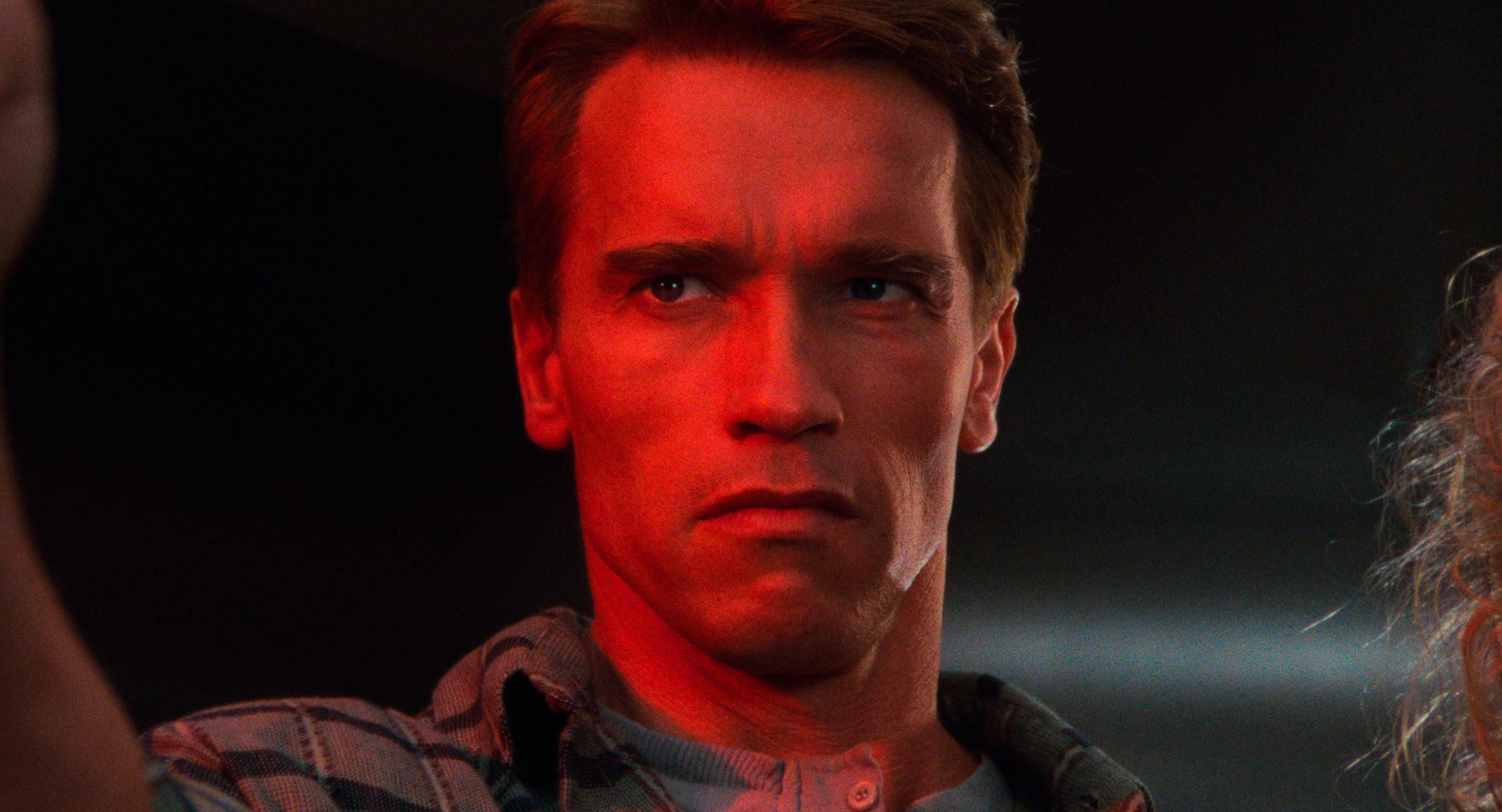
75/100Before watching Studiocanal’s new restoration of the 30-year-old science-fiction adventure Total Recall, I had only vague memories of seeing it on opening night. I mean, I remembered that I hated it, but I wasn’t sure why. I was already a Paul Verhoeven fan based on RoboCop, though I didn’t know anything else about his work. I know I was put off by the scene where Arnold Schwarzenegger puts a bullet in a woman’s head and then yuks it up with one of his trademark murder jokes. Sure, the screenplay has taken pains to establish the character’s unforgivable duplicity, but that’s the problem: She’s disposable, and she’s a punchline. (No wonder Sharon Stone jumped at the chance to play a serial murderer of men in Verhoeven’s next film.) And I recall that I was annoyed beyond reason by the film’s climax, which involves a very sudden change to the environment on Mars. The science behind it struck me as insultingly preposterous. Still, I think what I really objected to, what actually offended me, was the light tone. After RoboCop, which struck me as an appropriately sick joke about fascist tendencies in American law enforcement (still in the news!), I guess I expected Verhoeven to treat Philip K. Dick’s epochal ruminations on human consciousness, thought, and identity with some gravity (cf. the similarly Dick-inspired Blade Runner) instead of turning them into a wildly overblown comic-book complete with an absurdly-ripped muscleman as the self-doubting superhero at the centre of the action. That’s on me; Looking back on Total Recall after three decades, I can see it more clearly. For Verhoeven, the cartoonishness is the point.

Look at it this way: it’s easy to read Verhoeven’s English-language output through the 1990s as a series of sardonic commentaries on American media. If RoboCop was a satire on cop movies, then Basic Instinct is a satire on police procedurals and Starship Troopers is a satire on military propaganda and Showgirls is a satire on, well, show business. That makes Total Recall, I guess, a satire on high-concept Hollywood action movies. Everything about it is vulgar, starting with the wildly inapposite casting of Schwarzenegger as our figurative everyman. The premise of the film is that an ordinary Joe’s world is turned upside-down when he learns that his entire life may be phony-that it could be the product of false memories implanted to obscure his former career as a planet-hopping secret agent with a Martian agenda. Dick’s protagonist was a government clerk-a “plain, dull” person who belatedly realizes he’s not plain or dull at all. Schwarzenegger was great as Conan and the Terminator, iconic killers you can see coming from a mile away. But how plain or dull is a perfectly sculpted Übermensch with biceps the size of toaster ovens? The whole concept of a secret identity falls apart if Clark Kent just looks like Superman in street clothes.

Does that matter, ultimately, when you’re making a summer blockbuster? David Cronenberg, one of a string of directors who had been attached to the Total Recall adaptation by Alien scribes Ron Shusett and Dan O’Bannon, must have felt the project being tugged this way when he worked on it back in 1984, first with William Hurt and later with Richard Dreyfuss expected to star. As Cronenberg tells the story, Shusett was interested less in Philip Dick than in “Raiders of the Lost Ark Go to Mars.” Producer Dino De Laurentiis stuck with the property until his DEG Studios went bankrupt, just as a Bruce Beresford version starring Patrick Swayze was getting off the ground. (By that time, even O’Bannon had abandoned the project.) It was reanimated when Schwarzenegger (who had sought the lead role for years) got Carolco to buy the rights and approached Verhoeven with what I have to imagine was an offer he couldn’t refuse. So give Arnold his due: whatever Total Recall is-part metaphysical science-fiction yarn, part colorful-but-dopey fantasy adventure-Schwarzenegger is as responsible as anyone for how it eventually turned out.
So Schwarzenegger plays Douglas Quaid, a construction worker who dreams of starting a new life on Mars, home to a near-future mining settlement riven by a civilian uprising against the corrupt ruling authority, led by the dictatorial Cohaagen (Ronny Cox). Frustrated by a thwarted desire “to do something with my life…to be somebody,” Quaid visits Rekall, a company that promises to implant memories that will make Quaid believe he has visited Mars without ever leaving planet Earth. The procedure goes awry, however, with Quaid suffering a “schizoid embolism.” As it turns out, Quaid has already had his memory wiped clean in order to eliminate evidence of his previous life as Hauser, an intelligence officer for the Martian government, in the form of memories that Rekall accidentally resurfaced. The revelation leaves Quaid confused but turns his life into the adventure he craved; he recovers a video recording left behind by his former self, who reveals that he turned against his employers and has designs on bringing down Cohaagen. Agent Hauser urges Quaid to hop on the next flight to Mars and await further instructions.
Verhoeven’s direction is resolutely over-the-top from the very first scene, a dream where Quaid imagines himself gasping for air on the Martian sandscape after accidentally shattering the glass of his face helmet. Verhoeven pushes in for an extreme close-up of Quaid’s face (in actuality a Rob Bottin puppet) as his eyes and tongue bulge painfully out of his head. The effect is almost too garish to be believed, but it turns out to be entirely in keeping with the overall tone of the film. There’s a security checkpoint with a full-body scanner that displays patrons’ skeletons at life-size. There’s a red-light district on Mars called Venusville, which Verhoeven based on Amsterdam’s red-light district and is home to a three-breasted hooker. There’s a resistance leader named George whose brother, Kuato, is in charge of the rebellion and is also embedded in George’s abdomen. (Citing Brian J. Robb’s Counterfeit Worlds: Philip K. Dick on Film, the film’s Wikipedia entry claims Kuato originated in one of David Cronenberg’s script drafts, though Shusett insists in Rob van Scheers’s Paul Verhoeven that he dreamed up Kuato after looking at pictures of conjoined twins.) Most notoriously, Verhoeven stages a scene where Quaid grabs a random bystander to use as a human shield against machine-gun fire.

Typically for Verhoeven, the results were too much for the Hollywood ratings board, which returned the film with the same X rating that graced his original cut of RoboCop, necessitating minor edits throughout before it could be delivered to theatres with an R. While RoboCop‘s excesses seem to shine a light on an American pathology, Total Recall‘s mayhem feels more purely indulgent-unless you think Verhoeven sees Quaid’s eagerness to adopt the trappings of a secret agent man, including his stone willingness to sacrifice others to save his own skin, as a symptom of pride, selfishness, and self-aggrandizement in the American psyche.
Too much? The screenplay is at least more clever than I realized back in 1990. The scene in which Quaid begins to realize that his life has suddenly become bigger than he ever imagined isn’t just an exposition dump that sets up the film’s remaining two acts-it’s a purely visual expression of Quaid’s feelings of inadequacy. As he watches the video presentation left for him by his alter-ego, Hauser (whom Schwarzenegger plays as a more confident, more charismatic, and more consequential version of Quaid), you can see Quaid marvelling at the man he once was and hopes he could become again. It’s no wonder he rushes to the Red Planet without worrying too much about what kind of trouble awaits him. It’s not just a chance to begin again; it’s an opportunity to realize the sort of fantasy Quaid has long nurtured for himself. Later in the film, a Rekall executive (Roy Brocksmith) shows up to inform Quaid that he has suffered that “schizoid embolism.” The exec says he has been injected into Quaid’s dream in a rescue mission, and warns that if he doesn’t snap out of his fantasy, Quaid will be stuck in “permanent psychosis” with his mind destroyed. What to do?
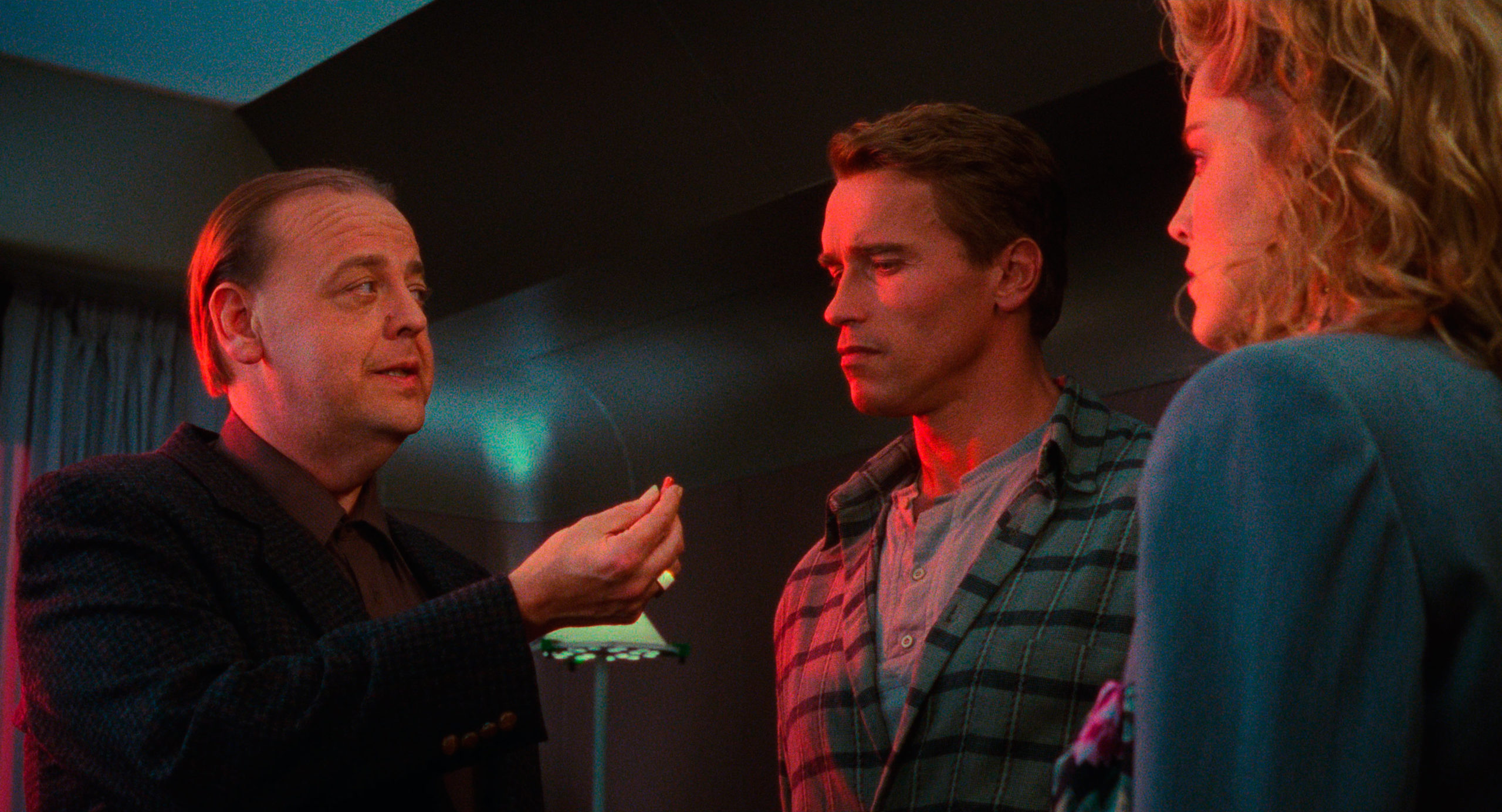

Total Recall is loud and gaudy, but Quaid’s situation is more poignant than the film at first seems to acknowledge. If Rekall’s fake experiences are as convincing as they’re reputed to be, then Quaid has no way of knowing whether the man is telling the truth. He has to interpret his perceived reality in one of two ways: he may be a double agent helping facilitate a righteous insurrection against an oppressive government; or he may be a sad body-builder with a dead-end construction job and an increasingly tenuous connection to sound mental health. The film doesn’t dwell on this point, but what Quaid’s offered is a false choice. It’s true that clues sprinkled throughout suggest that Rekall may well be telling Quaid the truth about his condition. (For one thing, the folks at Rekall seem to know exactly how Quaid’s Martian excursion is fated to unfold, supporting the idea that it’s a pre-scripted experience; for another, the film culminates in a happy ending with a fade to white, which seems deliberately suggestive in a way the expected fade to black wouldn’t.) Yet it seems clear that Quaid would experience a return to his former life as a spiritual defeat too dispiriting to contemplate-and what kind of movie would that be, anyway? While you could read this thirst for elevated sensation as a metaphor for moviegoing, to me, the existential implications are deeper. In the end, it’s like this: whether Quaid believes in himself or not, he has to believe in himself. That’s a profound observation, since it’s the same impulse that helps us get out of bed in the morning, however discouraging our circumstances may be. As Quaid himself puts it: “If I’m not me, then who the hell am I?”

THE 4K UHD DISC
StudioCanal returned to the original 35mm negative to create a new 4K master of Total Recall, a project that must have presented a special kind of challenge. The problem isn’t so much the film’s age as it is the era of its special-effects work. Many of its shots don’t involve special effects at all, of course, and of those that do, some of them were captured in-camera. Optical process shots nevertheless present an issue, as they’re at least one generation removed from the original camera negative in quality. That means they appear softer, with less dynamic range, a difference that should be glaringly apparent in a UHD and HDR presentation. The trick is to match the process shots as closely as possible to the camera-original material for the sake of consistency-without degrading the overall presentation. StudioCanal has managed that pretty well, as hue and saturation remain very consistent from shot to shot, despite the unavoidable shifts in picture grain and contrast.
Colors are exceptionally saturated-almost too saturated (the hot pink of Sharon Stone’s workout top is almost too intense to gaze upon directly), with skin tones sometimes tending towards the beet-red. (Those are deliberate creative decisions, of course, and Lionsgate assures that Verhoeven himself supervised this new “restoration.”) More troublesome to my eyes is the interaction between the pin-sharp film grain and the Dolby Vision color grade, which sometimes adds harshness to what should be an organic grain structure, especially in scenes with neon bulbs or other specular highlights. I don’t know how, exactly, you deal with this problem-I suspect the best solution will involve more carefully managing the HDR grade rather than simply cranking up the noise reduction-but I hope studios figure it out. I wish it had been possible to restore the edited bits of gore for an unrated release, but this new version is a definitive visual take on Total Recall.
Audio quality is fine if unexceptional. Though Total Recall doesn’t have the busiest sound mix in action cinema, there are plenty of directional audio effects across the front horizontal soundstage, along with occasional detours into the height channels (especially during the third act on Mars), and Goldsmith’s score sounds terrific in Dolby Atmos, with the musical orchestration, at least, taking advantage of the surround channels. Low-frequency effects are deployed sparingly but forcefully. Basically, the sound is wholly appropriate for the film’s vintage-remember, Total Recall was released on the cusp of the 1990s heyday of digital sound formats, just before sound designers were emboldened to create ever-more-active surround mixes.
The 30th-anniversary package offers one UHD BD, two BDs (one dedicated to special features), and a digital download code. Three new-to-this-release features are included on both the UHD and BD platters. “Total Excess: How Carolco Changed Hollywood” (59 mins., 1080p) purports to tell the story of Andrew G. Vajna and Mario Kassar’s mini-major studio, which grew to prominence with the release of Sylvester Stallone’s Rambo movies in the 1980s, plateaued on the back of hits like Total Recall, Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991), and Basic Instinct (1992), and then collapsed under the weight of the expensive failures of Showgirls and Cutthroat Island (both 1995). Unfortunately, neither Vajna (who died in 2019) nor Kassar (who presumably declined to be interviewed) appear on screen, though a number of their associates and creative collaborators show up, such as Verhoeven, Michael Douglas, Oliver Stone, editors Mark Goldblatt and Mark Helfrich, and film music producer Robert Townson. (Alan Parker, George Cosmatos, and Walter Hill appear in archival interview footage.) It’s entertaining enough, thanks to lots of footage from the films under discussion, but it feels more like an extended clip reel than any kind of definitive history.
“Open Your Mind: Scoring Total Recall” (21 mins., 1080p) foregrounds a discussion of Jerry Goldsmith’s score by a slate of interviewees including film music devotees Daniel Schweiger, Jeff Bond, and Lukas Kendall, as well as Townson again. Among the elements of Goldsmith’s work foregrounded here are his combination of orchestral and electronic instruments, his use of brass to underscore the frustration and anger of Michael Ironside’s character, and the difficulty orchestras ran into when it came time to play the complex music Goldsmith had composed. (Apparently the experience soured him on action films.) There’s also some talk about the similarity between Goldsmith’s compositions here and Basil Poledouris’s bombastic, percussive score for Conan the Barbarian, the suggestion being that Goldsmith may have been asked to emulate temp tracks from Conan.
“Dreamers Within the Dream: Developing Total Recall” (8 mins., 1080p) presents an audio-only interview with concept artist Ron Miller accompanied by an assortment of his illustrations for the film. He discusses the challenge of creating designs that are both scientifically plausible and visually interesting, but also takes a longer view of the project as a whole, recalling his year-long engagement with Cronenberg’s version of the film and talking about changes made after Schwarzenegger became the lead. Last (and least) among the new-for-UHD special features is a newly-created 30th-anniversary trailer (1:33) for StudioCanal’s remastered version of the film.
Holdovers from Artisan’s 2001 DVD special edition include an audio commentary with Verhoeven and Schwarzenegger, present on both BD and UHD. It zips along at a pretty good clip, although it’s not exactly bursting with information; Verhoeven and Schwarzenegger spend a lot of their time simply verbalizing what’s happening on screen and drawing attention to every ambiguous story beat that suggests Quaid may be living in a dream. In Schwarzenegger’s telling, he helped broker a quick-turnaround deal between De Laurentiis and Carolco once the former’s studio went out of business and then immediately met with Verhoeven about directing. Verhoeven explains that the bleak, bare-concrete style of many of the sets was based on the Brutalist architecture found on filming locations in Mexico City. He also reveals that the scene where the Rekall executive tries to convince Quaid that he’s still dreaming was inspired by Alfred Hitchcock’s Torn Curtain. After watching Michael Ironside shoot a woman in the back, Schwarzenegger chuckles at Verhoeven’s excess: “I love it. It’s one thing to shoot somebody. It’s another thing to shoot them in the back. And it’s another thing to shoot a woman in the back.”
Three more features are exclusive to the second BD. “Imagining Total Recall” (30 mins., 480p), also from the 2001 DVD, holds up surprisingly well. It’s the most comprehensive making-of feature in the package, combining EPK-style soundbites and B-roll from the production with latter-day cast and crew interviews. Shusett details the film’s long history in development, production designer William Sandell remembers nearly the entire crew getting sick in Mexico City, and VFX supervisor Eric Brevig and CGI director Tim McGovern describe the intricate and groundbreaking VFX, encompassing a ton of Martian miniature work and one of the first appearances of CG in a feature film. Arnold bitches about Carolco’s failure to promote the film aggressively until he leaned on the studio, and even Jerry Goldsmith shows up to describe his “fairly avant-garde, very difficult” score-and to answer critics who claimed it lacked a theme.
“Models & Skeletons: The Special Effects of Total Recall” (23 mins., 1080p), a Studiocanal production from 2010, documents some of the film’s key special effects scenes by way of interviews with Mark Stetson, who remembers renting a 20,000-square-foot warehouse for his company, Stetson Visual Services, to construct miniatures for the film, and Tim McGovern, the CGI Director at Metrolight Studios, creators of the X-ray skeletons at the security checkpoint. Stetson tells how various effects shots were designed and executed, highlighting the use of imagery front- and rear-projected (in one case using a miniature projector originally developed for The Abyss) onto tiny screens built into the miniatures themselves. He remembers some fears that the deep reds of the Martian landscape would bleed and bloom on VHS tapes but says Verhoeven was unbothered: “Paul said quite emphatically that he didn’t care about the video aftermarket.” McGovern goes into even more detail about the skeleton sequence, which was bedevilled by problems technical and otherwise before finally appearing flawless in the finished film. “We didn’t know to negotiate properly for screen credits,” he laments, noting that his name appears in the credits only on VHS versions of the film, and even then only because McGovern earned a Special Achievement Academy Award for his work, shaming Total Recall‘s producers into making amends. (No, his name isn’t in the credits on the UHD BD, either.) Finally, “The Making of Total Recall” (8 mins., 480p) is disposable vintage EPK fodder from 1990 aimed at interested but unconvinced moviegoers. It’s notable only for its brief comments from Verhoeven, Brevig, Ironside, Cox, Schwarzenegger, and the elusive Rob Bottin.
113 minutes; R; UHD: 1.85:1 (2160p/MPEG-H), Dolby Vision/HDR10, BD: 1.85:1 (1080p/MPEG-4); English Dolby Atmos (Dolby TrueHD 7.1 core), English DTS 2.0, French 5.1 DTS-HD MA, Spanish DTS 2.0; English SDH, French, Spanish subtitles; BD-100 + BD-50 + BD-25; UHD BD: Region-free, BD: Region A; Lionsgate
Requiem for a Dream
68/100Few films are anywhere near as well made-as fierce and committed-as Requiem for a Dream, which stands as a 20-year-old landmark in an especially fertile era of New York indie filmmaking and one of the most expertly executed feel-bad narratives in the history of popular culture. Darren Aronofsky is a hell of a director, but he’s always been a little, well, intense for my taste. He’s got vision and passion to spare, and he clearly inspires dedication and devotion from his actors, yet I always feel there’s something critical missing from the films themselves. If π is David Lynch without an angle on the truly bizarre and Black Swan is David Cronenberg without the painful psychological acuity, then Requiem for a Dream is John Waters without the sense of humor. I know Waters is friendly with Aronofsky, but imagining him watching this in a dark theatre and positively cackling at its most painfully outré gambits is what helps get me through its pitiless final act.
Based on a Hubert Selby Jr. novel, Requiem for a Dream is the story of four addicts. There’s Harry Goldfarb (Jared Leto) and his buddy Tyrone (Marlon Wayans), two small-time drug dealers whose lives spiral out of control when the supply of smack they’ve become physically, emotionally, and economically reliant on dries up. There’s Marion (Jennifer Connelly), Harry’s beautiful girlfriend from a wealthy family who sticks with him because, well, largely because he’s the antipode to everything she hates about her rich family. And, most importantly, there’s Harry’s mother, Sara (Ellen Burstyn), who shuts herself in a closet when she can’t deal with her son, who is about to pawn her TV set for drug money for apparently the umpteenth time. In the film’s opening scene, which plays out in an unbearably tense split-screen where you can see Harry wrestling with the TV on the right while Sara peers out through a keyhole on the left, the younger Goldfarb is already yelling at the elder through the locked door: “WHY YOU GOTTA MAKE ME FEEL SO GUILTY, MA???” “This isn’t happening,” Sara whispers. “It’ll all work out…. In the end it’s all nice.” And then the film’s title card literally falls on-screen from above, accompanied by the sound of a huge metal door slamming shut.

Subtle it isn’t. It’s almost playful, the way this prologue explicitly promises the audience an absolutely terrible night at the movies. You could say that Aronofsky plays fair with his audience by warning them here not to get too attached to these people. Or you could say it’s an example of self-aggrandizement, with a director loudly announcing how hard he is, he and his buddy Hubert, and how uncompromising their combined vision of humanity will be. I feel like this sort of macho filmmaking brio came into vogue a couple of years earlier, when Gaspar Noe announced the impending climax of I Stand Alone by displaying a title card reading, “You have 30 seconds to leave the theatre.” But where Noe identified a point of demarcation for a supposed contingent of sensitive viewers, Aronofsky turns the screws gradually over the course of 110 minutes, his editing tempo forever increasing and Clint Mansell’s musical backdrops-think Michael Nyman showing up at a party DJ’d by the Dust Brothers-growing more staccato, more nightmarish, with every cue.
I’m not saying Requiem for a Dream‘s aesthetic is completely gratuitous. Chemical dependency is a miserable affliction, and if Aronofsky’s work here serves as a PSA that helps any one person recover from a destructive vice or stay clean in the face of temptation, then it’s found its reason to exist. And it’s not merely an anti-heroin screed. By giving Sara Goldfarb’s narrative equal weight to Harry’s, Requiem does more than provide a showcase role to an actress who deserves one: It throws a spotlight on a different kind of miserablism, one that’s not so often romanticized by the movies simply because its victims tend to be older women rather than waifish youths. With little but meals and bedtimes breaking up her days and nights, the widowed Sara is a compulsive TV viewer, gravitating particularly to a serial infomercial hosted by smarmy self-help huckster Tappy Tibbons (Christopher McDonald). Sara lives alone, and something about her loneliness, decoded through the Videodrome-esque signal she seems to receive from Tibbons, compromises her rational thinking.
After receiving a phone call from some sort of audience-recruitment firm for TV shows, Sara convinces herself she’s about to be invited on stage by Tibbons himself. (“It’s a reason to smile,” she says. “It makes tomorrow all right.”) Her determination to lose enough weight to wear a favored red dress to the taping leads her to request diet pills from her too-acquiescent doctor. She loses weight, all right, as her addiction to speed bullies out her addiction to food and drives a worsening series of hallucinations. I’m not necessarily a fan of Aronofsky’s visualization of the inside of her head-images of cookies, cupcakes, and donuts falling from the ceiling and her refrigerator becoming sentient feel like rejects from an entirely different kind of movie about fat people-but Burstyn is astonishingly good in the role. Aronofsky told Vulture about shooting the scene where Harry visits Sara in her apartment and is astounded to realize she’s been prescribed a powerful cocktail of stimulants and depressants that has her as strung out as he is; the director says one shot of Burstyn’s performance came back soft because DP Matthew Libatique was crying behind the camera and had fogged the viewfinder so that he couldn’t properly check focus. That kind of performance.

Aronofsky and Selby have claimed that the film is an illustration of different kinds of addiction rather than a scary fable about four junkies’ worst-case scenarios unfolding in parallel-which is precisely the kind of thing you’d say to avoid being called out as the scolds who made the most wildly over-the-top anti-drug propaganda of all time. But it checks out. Aronofsky’s acerbic visuals make an explicit connection between Harry’s illicit drug use and Sara’s social-norm highs. One quick-cut montage progresses pointedly from the familiar dope-film iconography of rolled-up dollar bills, dilating pupils, and tiny plastic packets full of white powder to diet pills, coffee grounds, and a repeated sip from a mug that sets time racing. Requiem for a Dream is also interested in the intersection between addiction and exploitation, showing how Marion is coerced into a downward spiral where she engages in prostitution in exchange for a steady supply of drugs. As she leaves the apartment of one of her sources, Clint Mansell’s mournful, Kronos Quartet-driven music drives her down the hallway and into an elevator to ground level before she vomits on the street. Other characters have their own inflection points that send them downhill. For Harry and Tyrone, it must be their decision to deal drugs, thus profiting off the miseries of others; they realize too late that their souls are in the same jeopardy as those of all the other dopeheads out on the streets.
What bothers me the most about Requiem for a Dream is that it seems so excited about the requiem and so lackadaisical about the dream. An early sequence returns to the split-screen format to show Harry and Marion in bed, murmuring sweet nothings from pillow to pillow. The standard critical rap on a scene like this is that the frames-within-the-frame isolate the characters from one another, showing how each remains an island despite their yearning for some kind of metaphysical connection. Aronofsky and his editor, Jay Rabinowitz (best known at the time for his work on Jim Jarmusch films), however, have a more lyrical touch than that. In some moments, the double-framing actually seems to close the space between them; in others, one image shows fingers touching skin in extreme close-up as one of the lovers appears in profile in the frame beside. Libatique cites the scene’s “cubist feel.” These are beautiful images. He’s a charming loser and she comes off as a poverty tourist, but as long as they cherish that kind of beauty, you can at least understand why they’re together.

It’s by far my favorite scene in a film that could have used more moments of grace instead of shoving past such delicate interludes to reach almost cartoonish story beats. Tyrone, for example, is a very broadly-drawn character. His big scene involves a nude woman cooing, “Come back to bed, baby” as he zones out, imagining himself as a young boy falling into his mother’s arms. The Oedipal connotations are, presumably, deliberate, as is the reference to exploitation films where Black men prove themselves between the sheets as well as in the streets. A vertiginous sex scene, the camera spinning in circles over the bed, seems engineered to highlight Tyrone’s sleek virility and his lady’s bone structure. Wayans’s performance is direct and affecting, though Tyrone is hemmed into an uncomfortably flat role as a jive-talking sidekick. I appreciated the deaf drug dealer who speaks to Tyrone in sign language, but the only other African-American character of note is Keith David’s Big Tim, a sexually voracious pimp who deals in “pussy” rather than money. (“He’s hooked on the thang, man,” Tyrone explains.)
Requiem for a Dream is hardly race-agnostic. Tyrone’s Blackness gives him a presumed role to play in the drug world, where he negotiates on behalf of Harry and Marion, and it becomes a frightening issue when he ends up, inevitably, at the mercy of racist prison guards. Yet the picture’s willingness to deal in racial stereotypes complicates things. Big Tim is written as Black for the sake of sensationalism-it’s clear that Selby believed it gives Marion’s surrender to his sexual demands an extra transgressive charge. (In the book, this is explicit: Selby has Marion chuckle as she thinks about her family’s reaction if they knew she was “making it with a schvartzer.”) David is nonetheless excellent in the role, investing Tim with a truly wicked variety of charm that could make him a likable villain if he weren’t a literal sexual predator. And none of this, by the way, is to suggest that Tyrone isn’t sympathetic. I believe the guy when he insists, “All I want out of life is a little bit of peace and happiness, that’s all.” Tough, because what Requiem for a Dream does best is strip away happiness-it may be the single most punitive film ever made. Though I wouldn’t say it lacks empathy, it’s short on sensitivity. It is ungenerous. Its horror-show flourishes are crass, its sensual excesses vulgar, and its single-minded bleakness marginalizes its characters. They become soulless caricatures, defined by their vices and shoved into corners by the exigencies of the narrative in which they’re trapped.

It boils down to this (spoilers if such things can be spoiled): a drugged-up Sara Goldfarb shows up uninvited in the lobby of Tappy Tibbons’s TV studio, demanding to know when she’s going to be on television. It’s an effective scene because it forces us to see two sides of the confrontation at once. We understand the chain of events-loneliness, depression, addiction-that has led her to the brink, but the office workers see her behavior as a complete non sequitur. Their solution, which is to call in the authorities for help, is inspired by ignorance rather than malice, though it may as well be a death sentence for Sara. At the same time, Tyrone and Harry are being processed for incarceration by sadistic, racist authorities. Eventually, Aronofsky is cutting from the distressing sight of a helpless Sara being prepped for electroconvulsive therapy to a scene of a woman in a dark and crowded room applying lube and a condom to a double-ended dildo she’s about to share in a sex act with a clearly miserable Marion. It’s a viscerally repellent image undergirded by the quick see-saw escalations of Mansell’s slasher-movie parody score and the nasal, chattering roar of a gallery of piggish Patrick Bateman types crying out for their bread and circuses as an old man hisses excitedly, “Ass to ass! Ass to ass!”
The ensuing sexual display is juxtaposed with the image of Tyrone stirring a vat of food in the prison cafeteria while a supervising warden taunts him with lines like, “You’ve got a rotten attitude.” Said Warden is played, for some reason, by Selby himself; when Aronofsky cuts back to a close-up of Marion’s face during her performance, it’s Selby’s contemptuous snarl that we hear as her body jerks and her eyes roll: “That’s it. Nice and easy. Mashed potatoes.” (Connelly later called the experience “draining, sad, and uncomfortable.” Same here.) The visuals are matched in intensity by the audio, with lines of dialogue edited to fall into sadistic rhythm with the jagged musical passages. Thanks to Brian Emrich’s crazily detailed sound montage, Requiem for a Dream would almost work as radio. Meanwhile, we learn that the infected hole near Harry’s elbow where the drugs go in has necessitated the amputation of his entire arm; and so this multifarious tableau of abject degradation climaxes as a bone saw connects with flesh and sprays blood across Harry’s face, a flourish that qualifies Requiem for a Dream quite literally as a splatter movie.

The thing is, the moment doesn’t come as an extension or amplification of the horror but as a relief: Just as we process what we’re seeing, the image fades to white and we realize, somehow, that it’s over. Requiem for a Dream has done its worst, and the credits will roll and we can get on with our day. As well crafted as it is, that long climactic sequence is so aggressive, so intrusive on anybody’s sense of well-being, that I can’t imagine how shocking it must be for an audience that takes it at face value rather than gaping from a safe emotional distance at the sheer belligerence of it all. That’s the thing about Requiem for a Dream-it’s simultaneously so many things at once, and it’s often engaged in a contradiction of itself. It’s an alienating arthouse bummer and a mainstream home-video success. The MPAA ratings board rejected it as too extreme for general release and Ellen Burstyn’s performance earned an Oscar nomination. It’s an extraordinary feat of cinematic craft and it’s a risible glumfest. It would deserve to be laughed off the screen if not for the obvious depth of feeling driving its performances. The movie is grimy and hectoring, vivid and audacious. It’s both narc and hipster, the cool kid and the capital-E Establishment. Anyway, Aronofsky captures an awful lot of exquisitely-imagined pain on film. But I say pain is spectacle, and spectacle is easy. Big screens and Dolby sound systems love pain because they’re built to overwhelm; like too much of our pain, they’re bigger than we are. Less common in the cinema but more precious are genuine expressions of beauty, charity, and hope. All I can really affirm is that, in the end, Requiem has so much to do with pain and so little to do with hope that I sort of regret having watched it a second time.
THE 4K UHD DISC
Lionsgate, caretaker of the erstwhile Artisan Entertainment catalogue, has brought Requiem for a Dream to UHD BD in time for the film’s 20th anniversary. The film is presented here in its “director’s cut,” meaning it represents the version that went into limited release without a rating after the MPAA threatened it with an NC-17. (Although this cut isn’t any longer than the R-rated alternative, it contains certain offending shots that had to be replaced to get the rating.) The transfer, narrowly letterboxed to the correct 1.85:1, is flat-out gorgeous. It’s not likely to be the sharpest 4K disc on your shelf, but it does appear to have extracted every lick of picture detail from the 35mm camera negative. The image is fairly thick with organic grain and natural color; I’d imagine there might have been a temptation to over-saturate the rich primaries of the film’s palette, but they’re dialled in tastefully and to appropriately film-like levels. Similarly, the Dolby Vision/HDR grade has been executed with restraint. It feels like the presentation often accesses the full dynamic range of the camera negative without allowing the image to pop in ways that were never intended. The new transfer captures Libatique’s painstaking manipulation of color temperature better than ever, and the lighting effects that dominate the film’s climactic sequences, which had an oversized impact on a theatre screen, are intensified by the increased contrast. I hadn’t seen the film since its New York theatrical release and, for what it’s worth, it looks here almost exactly like I remember it.
Requiem for a Dream has also gotten a new Dolby Atmos remix, something I would have expected to find superfluous given the inherent density of the film’s audio. Quite the opposite, this mix has so many elements in it that it convincingly fills the Atmos soundfield. My set-up uses front height speakers (not ceiling speakers), which isn’t an ideal configuration, so I was surprised at how much Requiem for a Dream benefitted from the Atmos treatment. Rather than cluttering up the mix with directional FX (though sounds can be heard circling the room in certain scenes), this track uses sound designer Brian Emrich’s multitude of sonic subtleties to build up atmosphere, generate a strong sense of space, and land the occasional jump-scare. Mansell’s heady score, whose instrumentation sometimes seems to be floating free somewhere above the screen, is treated as the worthy backbone of a smoothly-layered audio mix; one musical cue featured percussive sounds that ping-ponged up and down in the room, massively broadening my front soundstage.
Lionsgate pulled out some stops for this release, shelling out for three new documentary featurettes, all of them presented in native 1080p. “Ellen Burstyn on Requiem for a Dream” (16 mins.) has the actress remembering her extraordinary efforts on the film, such as the two-week period where she lost weight by eating nothing but cabbage soup and the ordeal of removing her prosthetics at the end of each shooting day: “The pain becomes part of the process.” She’s a terrific interview; this one had me Googling “ellen burstyn audio commentary” immediately to see if there might be more like this out there. In “Transcendent Moments: The Score of Requiem for a Dream” (17 mins.), Clint Mansell talks about his relationship with Aronofsky, who got him in the right frame of mind by telling him to think of Requiem for a Dream as a monster movie, which made him decide “Lux Aeterna” would be the monster’s theme. (Mansell insists the funereal motif has “a twinge of hope in it”-the kind of lie you tell yourself if you wrote the most depressing earworm in contemporary cinema, I guess.) He discusses hip-hop and dance music’s influence on his own score (in another life, he led the 1990s band Pop Will Eat Itself) and the process of sampling different sounds from various musical requiems for deployment during the film’s climactic sequence.
And in “Revisiting Requiem for a Dream” (13 mins.), Dr. Bruce Isaacs of the University of Sydney offers a critical appreciation of the film, appraising it as “that bold experiment that suggested a great capacity for [American] independent filmmaking to do something extremely experimental, sophisticated, and challenging.” To which I can only say, wow-it’s almost like the careers of John Cassavetes, David Lynch, and Charles Burnett never existed! Likewise new to this release is an edited collection of B-roll and interview footage dating to the film’s original production and upscaled to 1080p. We get little more than a glimpse of the film’s location shoot on Coney Island, and the tiny snippets from vintage interviews with Aronofsky, Burstyn, Connelly, producer Eric Watson, and Wayans are barely worth a look. (Truth in advertising: Leto says, “I think Requiem is going to be a ride into Hell.”)
The UHD BD additionally recycles material from previous physical releases, such as the audio commentary Aronofsky recorded back in 2000. He delivers a generous, somewhat personal monologue that recalls the golden age of LaserDisc commentaries. His detailed discussion of the film’s 10-minute long scene between Leto and Burstyn, especially the sly way he has Libatique’s camera cross the 180-degree line at one point so that it ends up shooting both characters from the dark sides of their faces, is a highlight. And he helpfully summarizes his take on the material: “Ultimately, Requiem for a Dream is about the lengths people go to escape their reality. And that when you escape your reality, you create a hole in your present, because you’re not there. You’re chasing off a pipe dream in the future. And then you’ll use anything to use that vacuum. So it doesn’t matter if it’s coffee, if it’s tobacco, if it’s TV, if it’s heroin, if it’s ultimately hope. You’ll use anything to fill that hole. And when you feed the hole, just like the hole in Jared’s arm, it will grow and grow and grow until eventually it will devour you.” A parallel commentary from Aronofsky’s longtime collaborator Matthew Libatique is less conversationally engaging but will be catnip for cinematographers and cinematography fans. Discussion of the production’s choice of camera bodies and lenses and his own decisions on lighting and color filtration for individual scenes are dated to some degree, given the quick advance of filmmaking technology, but still shed ample light on his creative process. The overall tone is somewhere between film-school guest lecture and ASC Master Class, so if lines like “We pulled Fuji 500 a full stop for a softer, less contrast-y feel” set your heart a-racin’, this will be an excellent way to spend part of your afternoon.
Since the previous Requiem for a Dream BD comes as a bonus in the same box, purchasers have access to a separate set of standard-definition extras as well. “The Making of ‘Requiem for a Dream'” (35 mins.) offers up a wealth of behind-the-scenes clips from both production and post, including footage of the Kronos Quartet recording the score, with Aronofsky’s descriptive voiceover helping keep the viewer oriented. “Memories Dreams & Addictions” (20 mins.) is a rather philosophical discussion between Burstyn and Selby that begins with the author’s assertion that “36 hours before I was born I started to die.” He explains that, while still in the womb, he experienced brain damage due to cyanosis (that’s when the umbilical cord gets wrapped around the baby’s neck and impairs blood flow to the brain), and the conversation just rolls from there. It reaches a kind of culmination when he admits to being at once “a frustrated teacher” and “a frustrated preacher,” explaining, “I never wanted to just tell a story. I wanted to put the reader through an emotional experience.” Also featured is a clip (1 min.) of Selby on set, reading aloud from his novel to help Burstyn prepare for a scene.
The balance of the platter is given over to deleted scenes, trailers, and TV spots. In the longest clip, running three minutes, Wayans is allowed to improv as the camera rolls and performs in character as Jar-Jar Binks (The Phantom Menace had just come out). Almost as long is an extended take of Selby’s prison guard mocking Tyrone as he mixes mashed potatoes, also running about three minutes and apparently made up of ad-libs. There’s a substantial scene, too, where Harry and Tyrone compare notes on their mothers, followed by a phone call from Harry to Sara, along with a raft of shorter clips that show how Aronofsky and Rabinowitz’s penchant for split-screens could have been taken to greater lengths, splitting the screen into as many as six areas. (In one of the clips, Leto, Connelly, and Wayans appear in a triptych, appearing to glance sheepishly at one another after Marion makes a modest proposal: “Why don’t we stop using?” It made me laugh out loud.) Unused clips from Christopher McDonald’s shot-on-video performance as TV’s Tappy Tibbons (running 5 minutes in total) are also available, in case you can’t get enough of him. Two 90-second trailers and two TV spots (one :30 and one :15) show how Artisan struggled to position the film without making it look like a total downer; three out of four replace the Mansell score with a jangly Moby track. In another blast from the past, the disc features a 90-second trailer for Monster’s Ball, a movie I had forgotten existed. (Well, now I remember. And so do you.)